As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to revolutionise the transportation sector, food delivery companies are beginning to realise significant savings and sustainability benefits by incorporating EVs into their fleets. Not only do electric scooters and bikes help businesses achieve their green goals, but they also enable substantial cost reductions, particularly in fuel and maintenance. This article explores how EV adoption can benefit food delivery companies with detailed data, case studies, and strategies for maximising savings.
Lower fuel costs:
Fuel costs are one of the largest expenses for food delivery companies. However, switching to EVs can drastically cut down on these expenses:
- Petrol/Diesel Vehicles: A typical food delivery vehicle running on petrol or diesel may consume ₹300 to ₹500 worth of fuel per day, covering 100-150 km.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): In contrast, an EV covering the same distance may consume just ₹50 to ₹100 worth of electricity.
- Savings:
- Daily Savings: ₹200 to ₹400 per vehicle.
- Annual Savings: ₹60,000 to ₹120,000 per vehicle (assuming 300 working days).
This is a substantial amount, especially when scaled up across multiple vehicles in a fleet.
Reduced maintenance costs:
Electric vehicles also come with lower maintenance requirements compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles:
- ICE Vehicles: For petrol or diesel vehicles, the annual maintenance costs (including oil changes, filter replacements, etc.) can range from ₹10,000 to ₹15,000.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): EVs typically incur much lower maintenance costs, with annual expenses for tire rotations, brake checks, and other minor repairs amounting to ₹2,000 to ₹5,000. Savings:
- Annual Maintenance Savings: ₹8,000 to ₹10,000 per vehicle.
Government incentives:
The Indian government has rolled out various schemes to promote the adoption of electric vehicles, which can further reduce costs for delivery companies.
- FAME II Scheme: Under this scheme, electric two-wheelers can receive subsidies of up to ₹15,000 per kWh of battery capacity. For a 2 kWh battery, this could mean up to ₹30,000 in savings.
- State Government Incentives: Some state governments also offer additional subsidies, typically ranging from ₹5,000 to ₹15,000.
- Tax Benefits: Potential reductions in road tax or registration fees can save an additional ₹2,000 to ₹5,000.
- Overall Incentive Savings: The total savings from government incentives can range from ₹35,000 to ₹50,000 or more, depending on the specific vehicle and location.
Data comparison: fuel vs. EVs: Let’s break down the cost comparison between fuel-powered delivery bikes and electric vehicles:
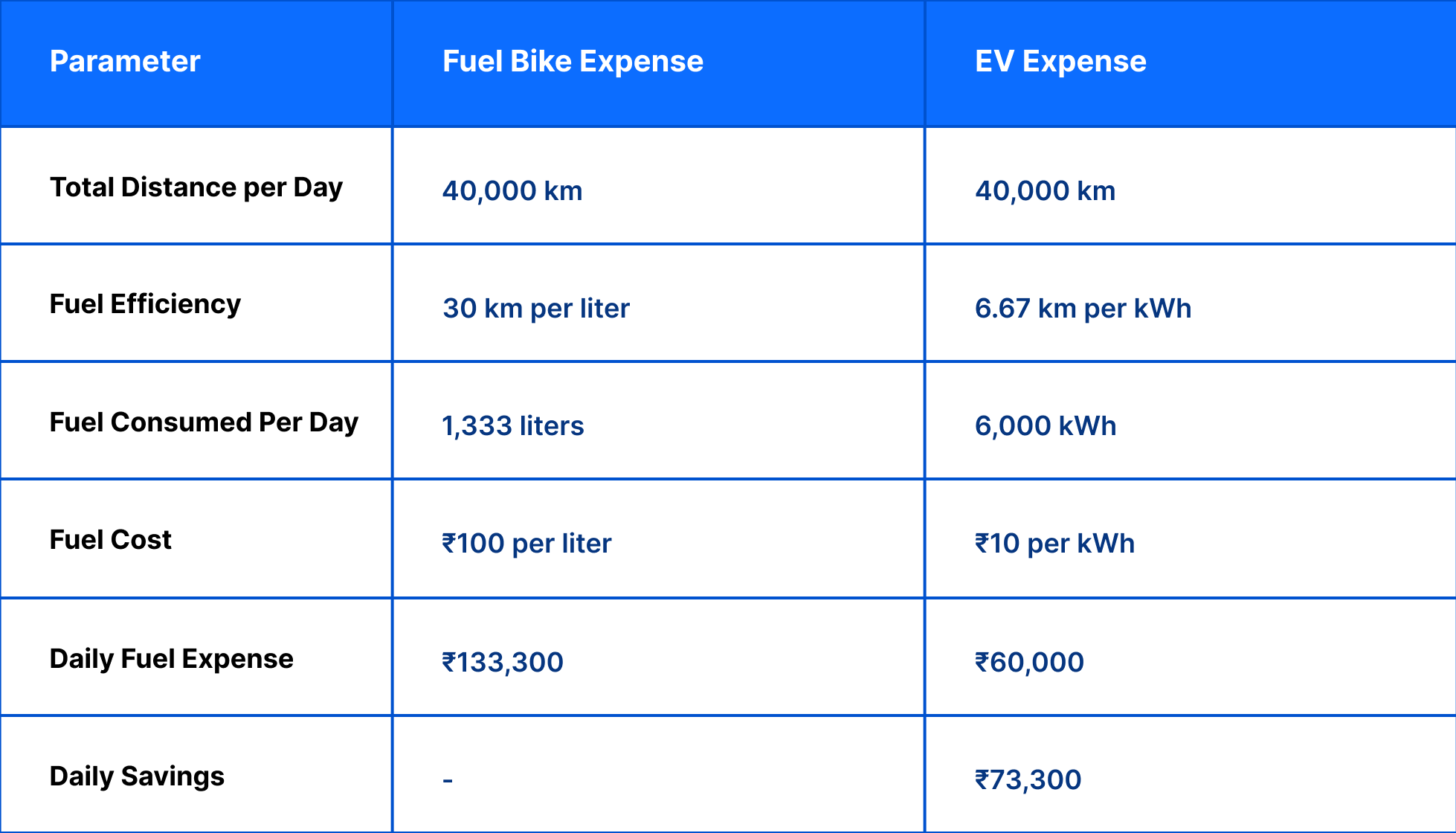
The savings are significant, with a daily difference of ₹73,300 between fuel-powered delivery bikes and EVs.
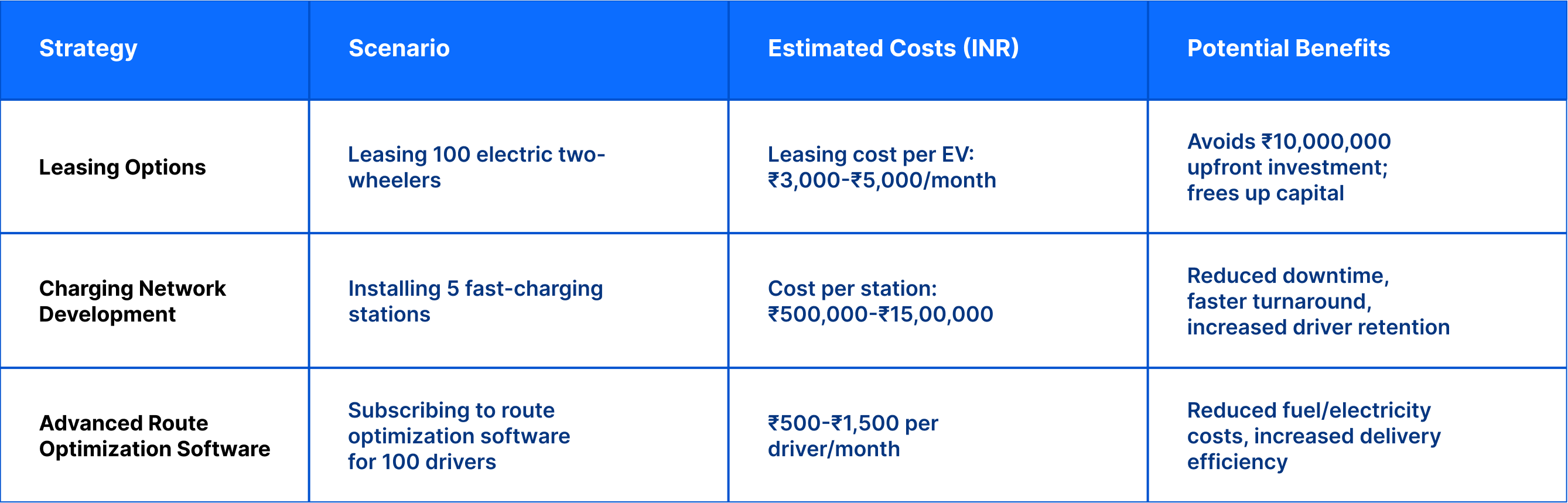
Collaborative strategies with partners: Estimated costs & benefits in INR
Here are some strategies that food delivery companies can use to enhance cost-effectiveness and improve EV adoption through collaborations:
Case studies of success in EV adoption
- Swiggy: Swiggy aims to shift its entire fleet to electric vehicles by 2030. The company has already started introducing the Swiggy XL EV fleet, which consists of custom-built electric vehicles for bulk orders. This transition will lead to both operational and environmental benefits.
- Domino’s Pizza: In 2023, Domino’s added 800 Chevrolet Bolt EVs to its fleet, creating the U.S.’ largest electric pizza delivery fleet. This initiative aims to boost delivery efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.
- Zomato: Zomato has publicly stated its ambition to make all deliveries 100% EV-based by 2033, focusing on achieving net-zero emissions across its operations.
- Zepto: Zepto has partnered with Battery Smart to tap into over 1,000 battery-swapping stations across 30 cities. This collaboration aims to deploy 10,000 new EVs into Zepto’s fleet in 2024-2025, improving operational efficiency and minimizing downtime.
Electric vehicles are not only a sustainable solution for food delivery companies but also a financially beneficial one. By adopting EVs, delivery companies can significantly reduce their fuel and maintenance costs while also benefiting from government incentives. Furthermore, through strategic collaborations, such as leasing EVs or setting up charging networks, companies can scale their operations in a cost-effective manner while reducing their carbon footprint. As EV adoption increases, we can expect to see more and more food delivery companies following the lead of pioneers like Swiggy, Domino’s, and Zomato in transitioning to greener and more cost-efficient solutions.
.jpg)

