Electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a popular and eco-friendly alternative to traditional gas-powered cars. With advancements in technology, EVs have become more accessible, offering a range of options for drivers. This article will provide a comprehensive guide to the different types of electric vehicles available in the market today.
1. Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
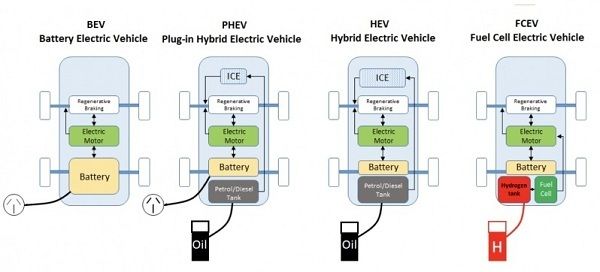
Battery Electric Vehicles, or BEVs, are pure electric vehicles that operate solely on electricity stored in a battery. These vehicles do not have an internal combustion engine and are powered by an electric motor. BEVs are an excellent choice for short-distance travel, thanks to their zero tailpipe emissions and low operating costs. As battery technology improves, BEVs are also becoming more practical for longer journeys. Notable examples of BEVs include the Hyundai Ioniq, Tesla Model 3, and Polestar 2.
2. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
Hybrid Electric Vehicles, known as HEVs, combine an electric motor with an internal combustion engine. HEVs utilize both petrol/diesel and electric power to propel the car, resulting in reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions compared to traditional gas-powered vehicles. Unlike plug-in hybrids, HEVs do not need to be plugged in for charging. The battery in an HEV is charged through regenerative braking and the internal combustion engine. The Toyota Prius, Chevrolet Volt, and BMW i3 are popular examples of HEVs.
3. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles, or PHEVs, feature a larger battery and a plug-in charging system. PHEVs can travel a limited distance on electric power alone before switching to the internal combustion engine. This dual power source gives PHEVs greater range compared to BEVs and HEVs. PHEVs offer the flexibility of using electricity for shorter commutes and the convenience of a gasoline/diesel engine for longer journeys. Noteworthy PHEVs include variants of the Toyota Corolla and RAV4, the Volvo XC40, and the BMW 3-Series.
4. Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles, also known as FCEVs, are an innovative type of EV that utilizes hydrogen as a fuel source. FCEVs convert hydrogen into electricity through a chemical reaction, with water being the only byproduct. These vehicles offer zero tailpipe emissions and have a range comparable to traditional petrol/diesel cars. However, FCEVs are currently more expensive than other EV types, and the availability of hydrogen refueling infrastructure is limited. Notable FCEVs include the Toyota Mirai and the Hyundai Nexo.
In conclusion, the world of electric vehicles encompasses a range of options to suit different needs and preferences. Whether you opt for a Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV), Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV), or Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV), you are taking a step towards a cleaner and more sustainable future. With ongoing advancements in battery technology and the expansion of charging infrastructure, the popularity of electric vehicles is set to soar.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. How long does it take to charge a battery electric vehicle? Charging times for BEVs vary depending on the charging station and the vehicle's battery capacity. It can take anywhere from a few hours to several hours to fully charge a BEV.
2. Do hybrid electric vehicles require regular maintenance like traditional cars? Yes, hybrid electric vehicles require regular maintenance, similar to traditional cars. This includes routine inspections, oil changes, and servicing of the internal combustion engine components.
3. Can plug-in hybrid electric vehicles be charged using a regular electrical outlet? Yes, PHEVs can be charged using a regular electrical outlet. However, it is recommended to install a dedicated charging station for faster charging and convenience.
4. Are there any government incentives or rebates available for purchasing an electric vehicle? Many countries and regions offer incentives, such as tax credits or rebates, to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles. These incentives vary depending on the location, so it's worth researching the specific incentives available in your area.
5. What is the driving range of a fuel cell electric vehicle? The driving range of a fuel cell electric vehicle depends on factors such as the vehicle model and the availability of hydrogen refueling stations. Generally, FCEVs can travel several hundred miles on a full tank of hydrogen.