In the rapidly evolving electric vehicle (EV) landscape, battery technology is as critical as the motor and chassis. For users, two key concerns dominate: safety and range. With the launch of the BYD Blade Battery in 2020, the company made a bold statement: build a battery that not only delivers energy but also redefines safety, structural resilience and lifespan. This blog dives deep into how the Blade Battery achieves these goals, why it matters for EV adoption, and what the future holds.
BYD has been active in battery research and manufacturing for over 29 years, developing its own proprietary cells and systems rather than relying solely on third-party suppliers. The Blade Battery, designed and manufactured by BYD’s subsidiary FinDreams Battery Co., Ltd., represents the culmination of those years of work, focusing on the chemistry of lithium iron phosphate (LFP) and innovative structural packaging.
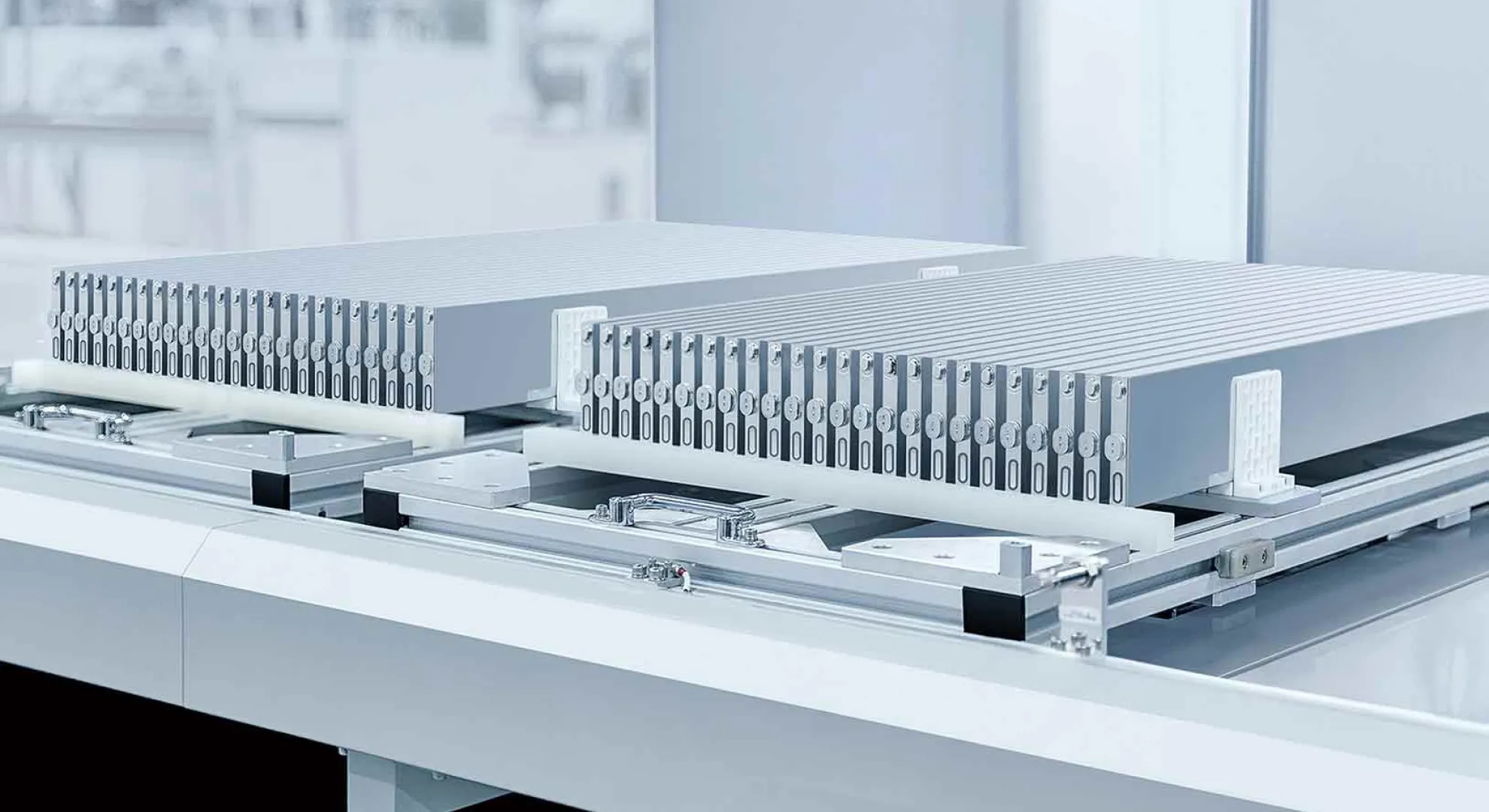
What Makes the Blade Battery Different
Chemistry: LFP with Enhanced Safety
At the heart of the Blade Battery is lithium iron phosphate (LFP). Compared to many ternary (nickel-manganese-cobalt, NMC) lithium-ion batteries, LFP offers inherent advantages in thermal stability: slower heat generation, lower heat release, and no oxygen release during breakdowns. These characteristics reduce the risk of thermal runaway — a key concern in EV batteries.
Cell Shape & Packaging: “Blade” Meets Structure
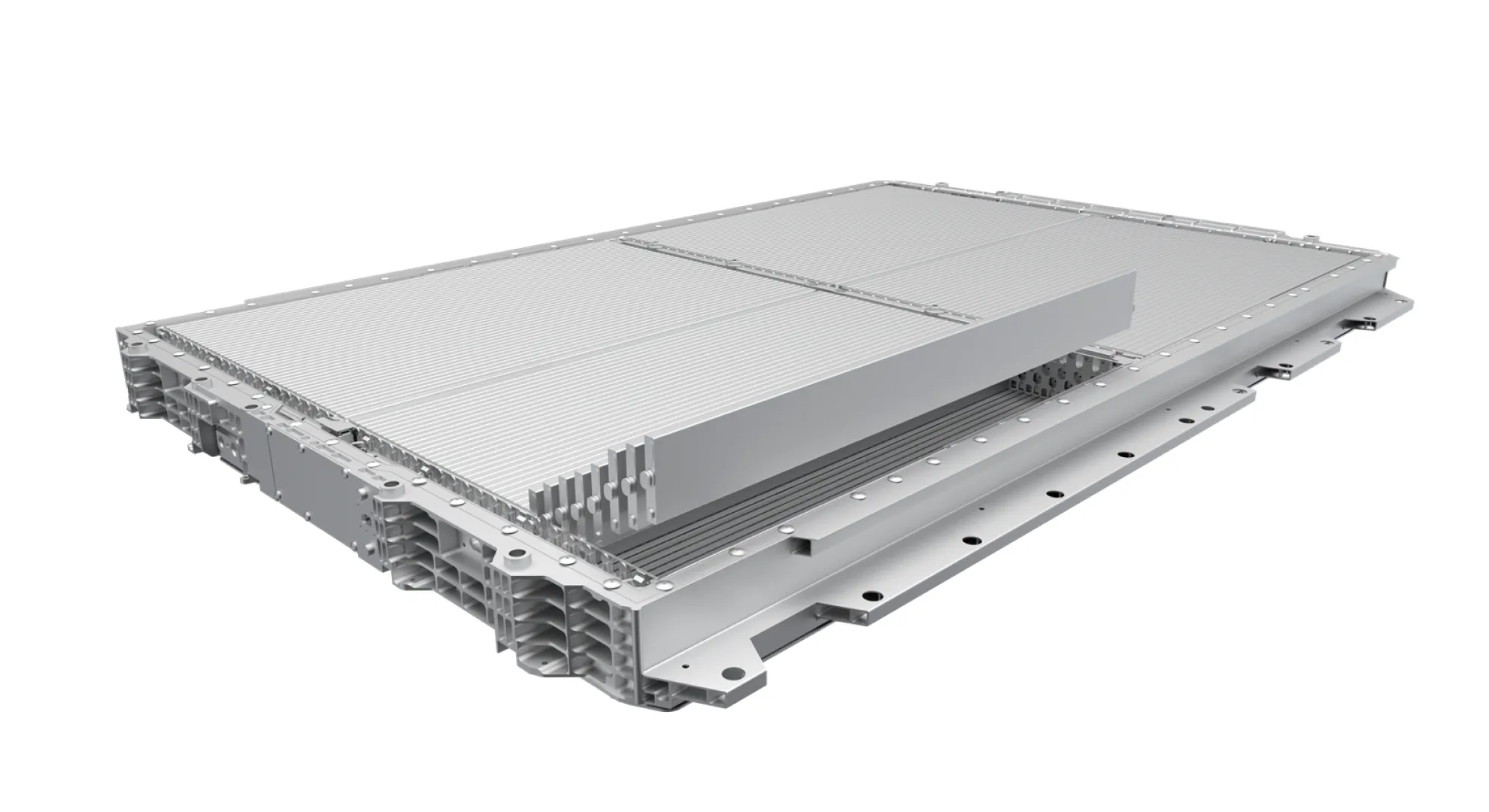
One of the most striking differences is the form factor. The single-cells are long and thin — commonly about 96 cm long and 9 cm wide in their “blade” configuration. These are inserted directly into the battery pack using a “cell-to-pack” (CTP) structure, eliminating many of the module layers found in conventional packs. The effect:
- Space utilization in the pack increases by over 50% compared to traditional LFP block batteries.
- Each cell becomes a structural beam within the pack, contributing to rigidity and crash performance.
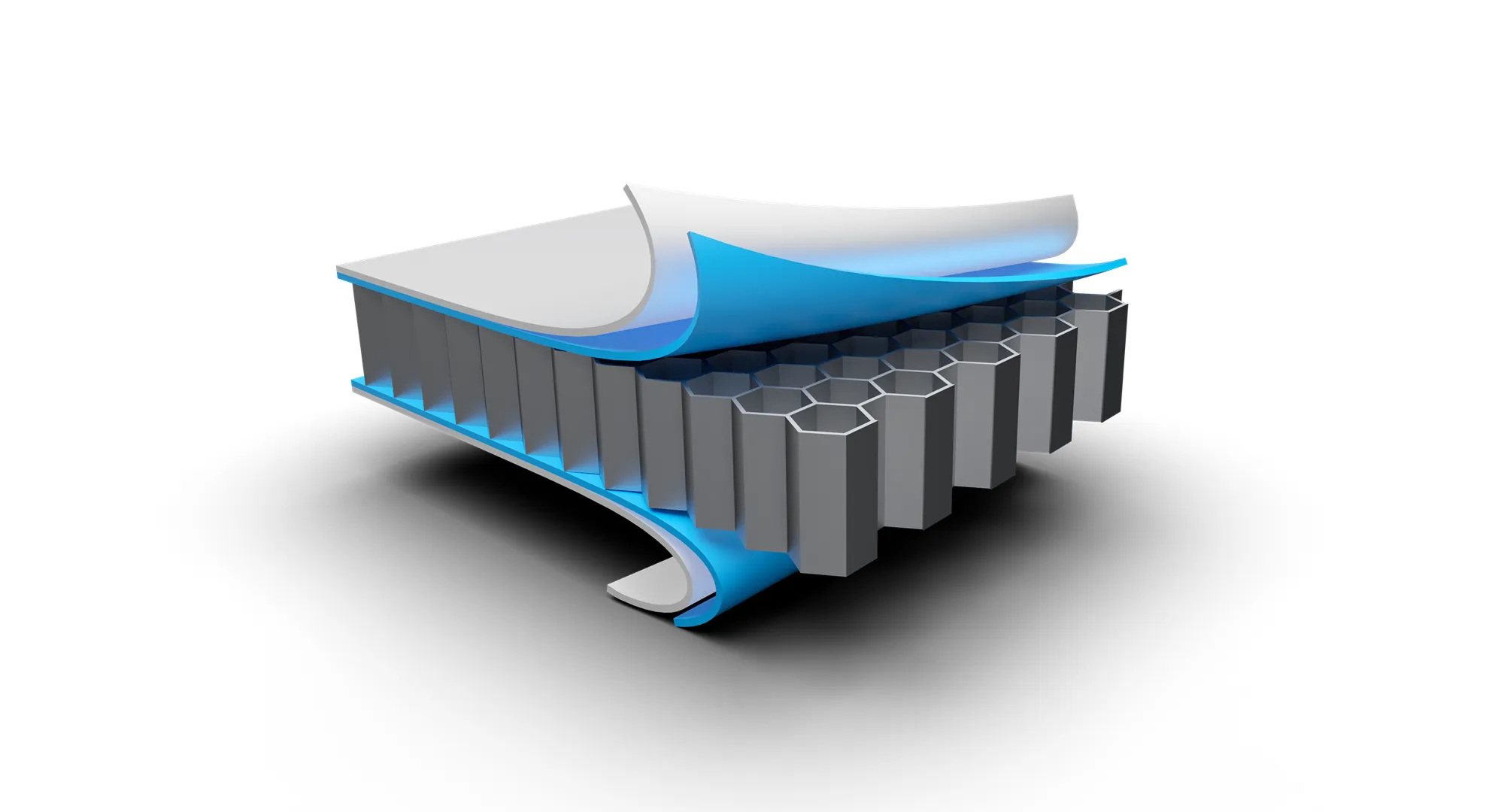
Rigidity & Crash Resilience
Beyond just storing energy, the Blade Battery pack design acts as part of the vehicle’s structure. The arrangement uses aluminum honey-comb-like framing and high-strength panels above and below the pack to bolster vertical rigidity and ensure forces from collisions are better handled. In extreme tests, the pack has been subjected to heavy loads equivalent to a 46-ton truck driving over it.
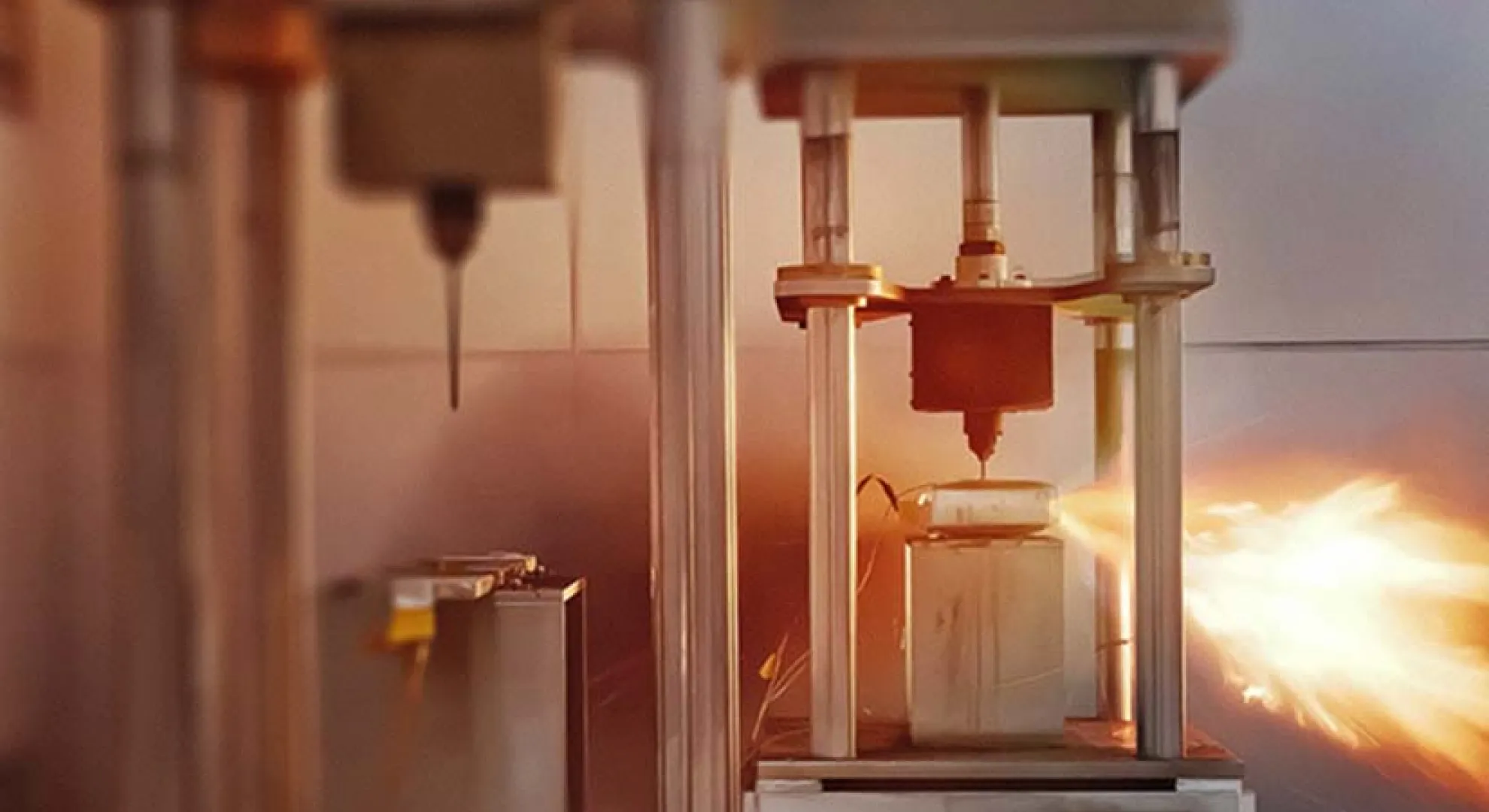
Safety Credentials in Depth
One of the most compelling aspects of the Blade Battery is how well it performs under extreme conditions.
- In a nail-penetration test (simulating a severe internal short circuit), the pack emitted no fire or smoke, and the surface temperature remained between 30-60°C — a far cry from ternary lithium batteries which may exceed 500°C.
- Additional tests included crushing, bending, heating in a furnace to 300°C, and overcharging the pack by 260%. None of these triggered a fire or explosion.
- These results build trust: when an EV is in a serious accident, the battery pack is no longer the weakest link.
Performance: Range, Charging and Longevity
- Higher Energy Density Through Space Efficiency: Because over 50% more of the pack volume is active cells (thanks to the blade format and CTP design), the energy density (on a volumetric basis) improves — giving longer driving range without necessarily increasing weight. Some of BYD’s models equipped with the Blade Battery have claimed ranges exceeding 700 km under CLTC test cycles.
- Fast Charging & Power Output: Although LFP chemistry historically charged slower than NMC, BYD has improved the Blade Battery’s parameters such that fast charging becomes feasible. For example, one source cites a rapid charge from 10% to 80% in 33 minutes.
- The blade cell design and pack architecture make more rapid discharge and recharge possible, supporting high power output for performance as well as rapid top-ups.
- Enhanced Cycle Life: Life-cycle is an important metric: how many full charge/discharge cycles can the battery endure before substantial capacity fade? BYD advertises more than 5,000 cycles for Blade Battery. This suggests pack longevity of substantially more than conventional EV batteries and implies a usable life of many hundreds of thousands of kilometers.
.webp)
Real-World Implications for EV Owners
- Safety Peace of Mind: For buyers concerned about battery fires or overheating — especially in hot climates or high-stress usage — the Blade Battery provides strong reassurance. Whether parked, driving or involved in an accident, the risk of thermal runaway is markedly reduced.
- Longer Life, Lower Total Cost: Because of the extended cycle life and structural resilience, EV models using the Blade Battery may retain more usable capacity over a longer period — reducing the worry of costly battery replacements, especially relevant in markets like India.
- Better Packing Efficiency: For manufacturers, more usable battery volume means either increasing range at the same battery size or reducing pack size/weight at the same range. For consumers, that can translate into lower costs, improved packaging (more cabin or cargo space) and less “range anxiety”.
- Suitability for India & Emerging Markets: In a market like India, where charging infrastructure is developing and ambient temperatures are high, the robust safety and thermal characteristics of the Blade Battery are especially relevant. Reduced risk of fire, better thermal management and fewer warranty concerns make it a strong proposition.
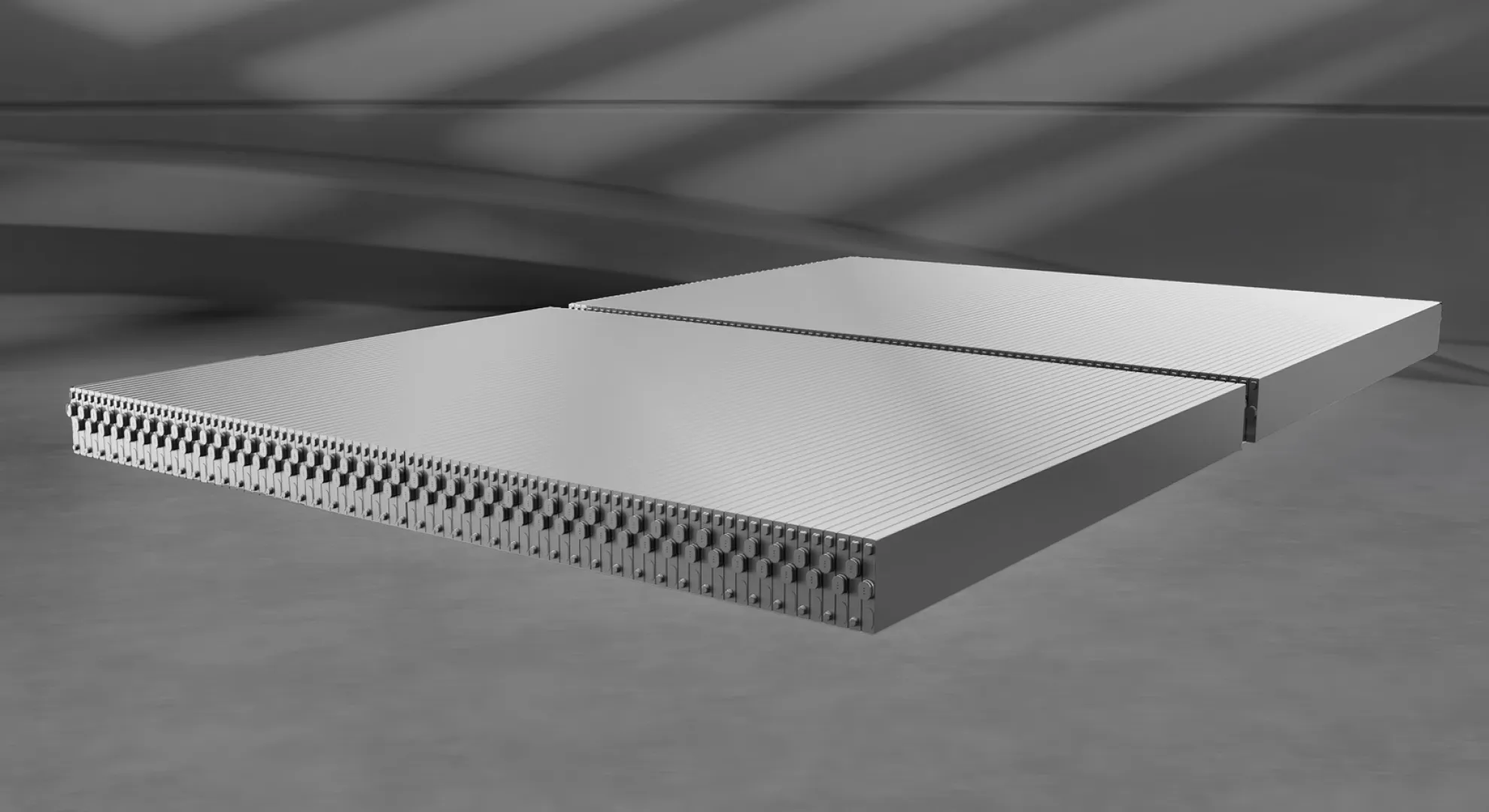
Challenges and Considerations
While the Blade Battery delivers numerous advantages, some caveats remain:
- LFP chemistry has a slightly lower energy density (by weight) compared with the latest high-nickel NMC chemistries. While the space efficiency compensates, weight efficiency may still lag.
- Fast charging at ultra-high rates still depends on supporting vehicle architecture, thermal management and charging infrastructure.
- As with all cutting-edge technology, long-term real-world data (over decades) are still being gathered, especially across varied climate zones and usage profiles.
What’s Next: The Future of Blade Batteries
Looking ahead, BYD is reportedly working on a next-generation Blade Battery upgrade. Reports suggest further improvements in energy density, cost reduction and perhaps higher voltage/charging platforms. As EV markets mature, batteries like this may become the standard rather than the exception.

Conclusion
The BYD Blade Battery is more than a battery — it is a paradigm shift in how EV batteries are conceived, designed and built. By combining the inherently safer LFP chemistry with an innovative blade-shaped cell and structural pack design, BYD has addressed three of the biggest concerns for EV owners: safety, range and longevity. Whether you are an EV enthusiast, fleet manager or content creator covering the future of mobility, the Blade Battery marks a major milestone worthy of attention. As EVs grow in popularity globally, technologies like this will underpin the transition from niche to mainstream.


